99 Bottles of Beer
"99 Bottles of Beer" is a traditional song in the United States and Canada. It is popular to sing on long trips, as it has a very repetitive format which is easy to memorize, and can take a long time to sing. In particular the song is frequently sung by children on long bus trips, such as class field trips, or on Scout and/or Girl Guide outings. The song is derived from the English "Ten Green Bottles".
The song's simple lyrics are as follows:[1][2]
Ninety-nine bottles of beer on the wall, Ninety-nine bottles of beer.
Take one down, pass it around, Ninety-eight bottles of beer on the wall.
The same verse is repeated, each time with one fewer bottle. The song is completed when the singer or singers reach zero. The last verse following the last bottle being taken down and passed around is "No more bottles of beer on the wall, no more bottles of beer. Go to the store and buy some more, 99 bottles of beer on the wall."
Contents |
Mathematically inspired variants
Donald Byrd has collected dozens of variants inspired by mathematical concepts and written by himself and others.[3] (A subset of his collection has been published as Byrd (2010, September).[4]) Byrd argues the collection has pedagogic as well as amusement value. Among his variants are:
- "Infinite bottles of beer on the wall". If one bottle is taken down, there are still infinite bottles of beer on the wall (thus creating an unending sequence much like The Song That Never Ends).
- "Aleph-Null bottles of beer on the wall". Aleph-Null is the size of the set of all natural numbers, and is the smallest infinity and the only countable one.
- "Uncountable bottles of beer on the wall". An uncountably infinite set is larger than a countable one; therefore, if only a countable infinity of bottles fall, an uncountable number remains.
Other versions in Byrd's collection involve concepts including geometric progressions, differentials, Euler's identity, complex numbers, summation notation, the Cantor set, the Fibonacci series, and the Continuum Hypothesis, among others.
On an episode of Malcolm in the Middle, on a way to the mathematics competition Macolm's classmates - the Krelboynes - sing a variation of this song stating "the square root of (number) of bottles of beer". Malcolm states to the camera that they are only at the nineties.
References in science
The computer scientist Donald Knuth proved that the song has complexity 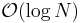 in his in-joke-article The Complexity of Songs.
in his in-joke-article The Complexity of Songs.
Computer programs exist to output the lyrics to the song. This is analogous to "Hello World" programs with the addition of loops. As with Hello World, this can be a practice exercise for those studying computer programming, and a demonstration of the differences between programming languages.
See also
References
- ^ Nyberg, Tim (2006). 99 Bottles of Beer on the Wall: The Complete Lyrics. Andrews McMeel Publishing. pp. 112. ISBN 978-0-7407-6074-7.
- ^ Baird, Kevin C. (2007). Ruby by example: concepts and code. No Starch Press. p. 25. ISBN 978-1-59327-148-0.
- ^ Byrd, Donald (2010-12-31). "Infinite Bottles of Beer: Mathematical Concepts with Epsilon Pain, Or: A Cantorial Approach to Cantorian Arithmetic and Other Mathematical Melodies". Indiana University, School of Informatics. http://www.informatics.indiana.edu/donbyrd/Papers/InfiniteBottlesOfBeer_FullVer.pdf. Retrieved 2011-02-20.
- ^ Donald Byrd (2010). "Infinite Bottles of Beer: A cantorial approach to Cantorian arithmetic and other mathematical melodies". Math Horizons: 16–17.
External links
- 99-bottles-of-beer.net - A vast compendium of computer programming languages and styles - each with the same output: the lyrics to this song
- Another variant of the above
- Modern Drunkard Magazine's list of the Top 86 Alcohol Songs of All Time, featuring "99 Bottles Of Beer On The Wall" by Atticus at #1
- 99 Bottles of Beer Screensaver - A free windows screensaver that displays the lyrics of the song and source codes of computer programs that output the lyrics